JavaScript 객체 지향 프로그래밍
생활코딩의 [JavaScript 객체 지향 프로그래밍] 을 학습하고 정리한 글입니다.
일부 이미지는 영상의 이미지를 캡처하였습니다.
[TOC]
물건을 보관한다.
물건이 많아지면 정리가 필요하다.
이때 각각의 특성에 맞게 정리해서 보관한다면?
코드들도 마찬가지다.
처음에는 그냥 보관하면 된다.
하지만 많아지면 정리해서 보관하면된다.
복잡한 코드들이 정리된다.
객체란?
서로 연관된 변수와 함수를 그룹핑하고 이름을 붙인것.
객체 vs 배열
// 배열
var memberArray = ['egoing', 'graphittie', 'leezhce'];
console.log("memberArray[2]", memberArray[2]);
// 객체
var memberObject = {
manager:'egoing',
developer:'graphittie',
designer:'leezhce'
}
// 읽기
console.log("memberObject.designer", memberObject.designer);
console.log("memberObject[designer]", memberObject['designer']);
// 수정
memberObject.designer = 'leezche';
console.log("memberObject[designer]", memberObject['designer']);
// 삭제
delete memberObject.manager
console.log('after delete memberObject', memberObject.manager);다음과 같이 Math 라는 객체로 다양한 기능을 불러서 사용할 수 있다.
console.log("Math.PI", Math.PI);
console.log("Math.random()", Math.random());
console.log("Math.floor(3,9)", Math.floor(3,9));이렇게 미리 정해두지 않았다면 개발이 힘들었을 것.
위의 random 처럼 객체에 속해있는 함수를 메소드라고 한다.
마찬가지로 어떤 비슷한 기능들을 모아서 우리도 다음과 같이 객체를 만들수 있다.
var MyMath = {
PI:Math.PI,
random: function(){
return Math.random();
},
floor: function(val){
return Math.floor(val);
}
}
console.log("MyMath.PI", MyMath.PI);
console.log("MyMath.random()", MyMath.random());
console.log("MyMath.floor(3.9)", MyMath.floor(3.9));만약 객체가 없다면 다음과 같이 선언을 하며 사용해야 한다.
var MyMath_PI = Math.PI;
function MyMath_random(){
return Math.random();
}
function MyMath_floor(val){
return Math.floor(val);
}this
this 는 객체 자기 자신을 가리킨다.
다음과 같이 sum은 kim 객체의 first 와 second의 합을 리턴하는 메소드이다.
var kim = {
name: 'kim',
first: 10,
second: 20,
sum: function(){
// return kim.first+kim.second; --- 1
return this.first+this.second; // --- 2
}
}
console.log("kim.sum(kim.first, kim.second)", kim.sum(kim.first, kim.second));
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());만약 1 처럼 만들었고 후에 객체의 이름을 kim 에서 lee로 변경한다면 오류가 날것이다.
그렇기 때문에 2 처럼 this를 사용하는 방법을 사용한다.
객체 공장
kim과 비슷한 lee 객체를 만든다.
그리고 third라는 속성을 추가하고 싶을때 각각의 개체에 적용해야하는 번거로움이 생긴다.
var kim = {
name: 'kim',
first: 10,
second: 20,
third: 30,
sum: function(){
return this.first+this.second+this.thrid;
}
}
var lee = {
name: 'kim',
first: 10,
second: 10,
third: 10,
sum: function(){
return this.first+this.second+this.thrid;
}
}
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());
console.log("lee.sum()", lee.sum());아래 코드를 보면 new 키워드를 통해 Date 객체를 생성해 반환해주는 것을 알수 있다.
var d1 = new Date('2019-10-16');
console.log('d1.getFullYear()', d1.getFullYear());
console.log('d1.getMonth()', d1.getMonth());우리도 이처럼 생성자(constructor function)를 통해 Date 처럼 동작하는 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
this.sum = function(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
}
var pak = new Person('pak', 10, 20);
var sin = new Person('sin', 10, 10);
console.log("pak.sum()", pak.sum());
console.log("sin.sum()", sin.sum());생성자의 역할
- 객체를 만든다.
- 그 객체의 초기 상태를 세팅한다.
prototype
JavaScript 를 prototype based language 로 부르기도 함.
전에 만들었던 sum 이라는 메소드를 일괄적으로 수정하고 싶다.
다음과 같이 변경하게 되면 메모리상 비효율적이다.
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
this.sum = function(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
}
pak.sum = function(){
return 'modified : '+(this.first+this.second);
}
sin.sum = function(){
return 'modified : '+(this.first+this.second);
}아래와 같이 Person의 prototype에 메소드를 추가하는 식으로 바꾸면 메모리를 절약할 수 있다.
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
Person.prototype.sum = function(){
return 'prototype : '+(this.first+this.second);
}또한 객체 별로 메소드를 변경할 수 있다.
pak.sum = function(){
return 'this : '+(this.first+this.second);
}이를 통해 알아보는 prototype의 특징
- 객체의 메소드
sum을 실행했을때 객체 자신이sum을 가지고 있는지 찾는다. - 만약, 없다면 그 객체의 prototype에서
sum을 찾는다.
class
ES6 부터 사용가능한 class 를 살펴보자
CanIUse 를 통해 ECMA 표준별 사용가능 브라우저 버전을 살펴볼수 있다.
Babeljs 를 통해 상위 버전의 JavaScript를 하위 버전의 코드로 변경할 수 있다.
(컴파일러 또는 트랜스파일러 라고 부름)
다음과 같이 class 키워드를 사용하여 생상자를 만들어본다.
class Person{
}class constructor
constructor 는 어떤 객체가 생성되기 직전에 호출되어 객체의 초기 상태를 지정해주는 함수 이다.
아래와 같이 constructor 함수를 통해 초기값을 설정할 수 있다.
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
// console.log('constructor');
}
}
var kim = new Person('kim', 10, 20);
console.log('kim ', kim);class 키워드를 사용한 문법으로 이전에 작성했던 Person 을 작성해본다.
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
sum(){
return 'prototype : '+(this.first+this.second);
}
}
var kim = new Person('kim', 10, 20);
console.log('kim ', kim);
kim.sum = function(){
return 'this : '+(this.first+this.second);
}
var lee = new Person('lee', 10, 10);
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());
console.log("lee.sum()", lee.sum());상속
Person 클래스에 함수를 추가하고 싶다.
만약, Person 이 기존에 작성된 라이브러리나 가져와사용한 코드라면 직접 수정하게되면 곤란한 상황에 빠진다.
다음과 같이 기존 Person 에 avg 메소드를 추가한 새로운 PersonPlus 클래스를 작성해보자.
괜찮은 방법 같지만 중복된 코드들이 많아진다.
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
sum(){
return 'prototype : '+(this.first+this.second);
}
}
class PersonPlus{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
sum(){
return 'prototype : '+(this.first+this.second);
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second)/2;
}
}따라서 extends 키워드를 이용하여 Person 클래스를 상속받고 중복된 코드를 제거하자.
class PersonPlus extends Person{
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second)/2;
}
}
var kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20);
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());
console.log("kim.avg()", kim.avg());super
이제 PersonPlus 로 만들어진 객체가 third 라는 속성을 갖고있길 바란다.
다음과 같이 PersonPlus 를 수정하면 될까?
class PersonPlus extends Person{
constructor(name, first, second, third){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
this.third=third;
}
sum(){
return this.first+this.second+this.third;
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
}이때 super 키워드를 사용할 수 있다.
super 는 2가지 용법이 있는데
- 바로 뒤에
()(괄호) 가 붙으면 부모 클래스의 생성자 ()(괄호) 가 아닌것이 오면 부모 클래스 가리킨다.
class PersonPlus extends Person{
constructor(name, first, second, third){
super(name, first, second); // super => 부모 클래스의 생성자
super.third=third;
}
sum(){
return super.sum()+this.third;// super => 부모 클래스
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
}객체간의 상속
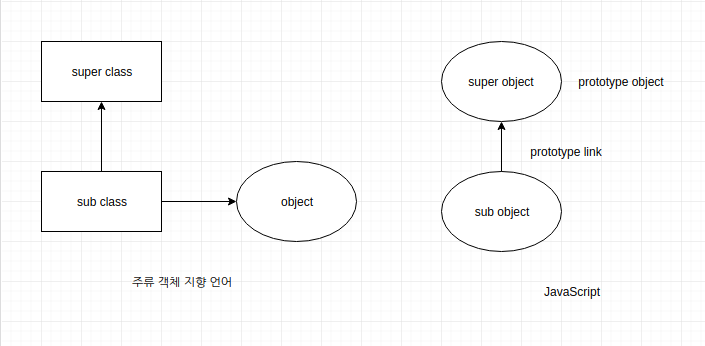
__proto__ 실제 표준으로 인정하지 않아 정석적인 방법이 아니다.
하지만 대부분의 브라우저에서 구현하기 때문에 사용할 수 있다.
다음과 같이 subObj 의 __proto__ 라는 속성을 통해 superObj 와 연결 시켰다.
var superObj = {superVal:'super'}
var subObj = {subVal:'sub'}
subObj.__proto__=superObj;
console.log('subObj.subVal =>', subObj.subVal); // subObj.subVal => sub
console.log('subObj.superVal =>', subObj.superVal); // subObj.superVal => super그후 subObj 의 superVal 의 값을 변경해보자.
subObj.superVal = 'sub';
console.log('superObj.superVal =>', superObj.superVal); // superObj.superVal => super실제 자신의 객체를 바꾼것이지 다른 객체를 바꾼것이 아니다.
더 좋은 상속방법은 Object.create 를 사용하여 다음과 같이 객체를 상속받는 것이다.
var subObj = Object.create(superObj);
subObj.subVal = 'sub';- 추가 내용:
debugger사용
debugger 를사용하면 브라우저가 해당 위치에서 실행을 멈추고 그때의 상태를 보다 상세하게 살펴볼 수 있다.
객체와 함수
모든 함수는 call 이라는 메소드를 가지고 있다.
function sum(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
sum.call(); // sum(); 과 같다call 의 인자로 kim 을 주게되면 그 순간 sum 의 내부에서 tihs 는 kim 이된다.
var kim = {name:'kim', first:10, second:20}
var lee = {name:'kim', first:10, second:10}
function sum(){
// this = kim;
return this.first+this.second;
}
sum.call(kim); // sum(); 과 같다call 의 매개변수
- 첫번째 매개변수는 그 함수의 this에 해당 되는 것
- 두번째 매개변수는 호출된 함수의 인자값으로 사용될 것
call 과 비슷한 기능을 가진 apply, bind 가 있다.
call 은 실행할때 컨텍스트의 this 의 값을 바꾼다.
bind 는 어떤 함수의 this 의 값을 영구적 바꾼 새로운 함수를 반환한다.
var kim = {name:'kim', first:10, second:20}
var lee = {name:'kim', first:10, second:10}
function sum(prefix){
return prefix+(this.first+this.second);
}
var kimSum = sum.bind(kim, '-> ');
console.log('kimSum()', kimSum());prototype vs _proto_
아래의 두 표현은 같은 의미다.
function Person(){}
var Person = new Function();JavaScript 에서 함수는 객체이다.
Person 함수를 선언하면 해당 객체와 prototype object 가 생성된다.
Person 의 prototype 은 prototype object 을 가리키고
prototype object의 constructor 은 Person 을 가리킨다.
또한 Person 을 통해 생성된 kim, lee 의 __proto__ 는 Person 의 prototype object 를 가리킨다.
kim 의 name 속성을 사용할 때 자신이 갖고 있는 속성이기 때문에 바로 사용한다.
하지만 sum 의 경우에는 자신이 가지고 있지않기 때문에
__proto__ 가 가리키고 있는 prototype object 에 가서 찾는다.

생상자를 통한 상속
PersonPlus 는 call 을 통해 Person 의 속성들을 상속받았다.
그러나 아직 sum 은 사용할 수 없다.
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
Person.prototype.sum = function(){
return this.first + this.second;
}
function PersonPlus(name, first, second, third){
Person.call(this, name,first,second);
this.third = third;
}
PersonPlus.prototype.avg = function(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.thrid)/3;
}
var kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20, 30);
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());
console.log("kim.avg()", kim.avg());1 처럼 __proto__ 로 연결 시킬수 있으나 비표준이기에 2 로 사용하는게 비교적 나은 방법이다.
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
Person.prototype.sum = function(){
return this.first + this.second;
}
function PersonPlus(name, first, second, third){
Person.call(this, name, first, second);
this.third = third;
}
// PersonPlus.prototype.__proto__ = Person.prototype; // 1
PersonPlus.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype); // 2
PersonPlus.prototype.constructor = PersonPlus; // 2
PersonPlus.prototype.avg = function(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
var kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20, 30);
console.log("kim.sum()", kim.sum());
console.log("kim.avg)", kim.avg());
console.log("kim.constructor", kim.constructor);kim 이 sum 을 사용하고 싶다면
Person 의 __proto__ 가 PersonPlus 의 prototype object 를 가리키면된다.

개념을 알아두고 사용은 class 를 사용하도록 하자.
'Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JavaScript] 연산자(Operator) (0) | 2019.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [JavaScript] 주석(Comments) (0) | 2019.04.04 |
| [JavaScript] 자료형(Data Type) (0) | 2019.04.04 |
| [JavaScript] 변수(Variable) (0) | 2019.04.04 |
| [JavaScript] 자바스크립트(JavaScript) 란 (0) | 2019.04.04 |